Marketing teams juggle multiple channels, assets, and campaigns simultaneously. When critical information lives in scattered tools like email threads, Slack messages, Google Drive folders, and individual desktops, marketing effectiveness suffers.
According to McKinsey research, employees spend nearly 20% of their workweek looking for internal information or tracking down colleagues for help – a challenge that hits marketing teams particularly hard given their reliance on diverse assets and cross-functional collaboration.
This fragmentation creates very specific challenges:
- Brand inconsistency when guidelines aren’t readily available
- Repeated questions that interrupt creative work
- Lost campaign insights that could inform future strategies
- Difficulty finding the most current version of assets
- Knowledge walking out the door when team members leave
An internal knowledge base addresses these challenges by creating a single source of truth for marketing operations. Let’s explore the most valuable use cases specifically for marketing teams.
Brand guidelines repository
Marketing teams maintain extensive brand standards including logo usage, color palettes, voice guidelines, and messaging frameworks. Without centralized access, these standards get applied inconsistently.
A knowledge base creates a living brand guidelines repository where:
- Visual identity elements remain accessible to everyone who needs them
- Brand voice guidelines help maintain consistency across channels
- Approved messaging frameworks guide all communications
- Updates reach everyone simultaneously, eliminating outdated versions
A practical example: A financial services marketing team created a brand guidelines repository in their knowledge base. When they refreshed their visual identity, they simply updated the central documentation and every team member, including external agencies, immediately accessed the correct assets. This eliminated the “Which logo version should I use?” conversations that previously consumed valuable time.
When agencies and freelancers need access to brand standards, controlled permissions ensure they see exactly what they need without exposing sensitive information.
Store brand assets effectively when they:
- Include approved usage guidelines and restrictions
- Represent the current brand standards
- Come with clear naming conventions for easy identification
Campaign documentation and lessons learned
Marketing campaigns generate valuable insights that often vanish after campaign completion. Teams repeat past mistakes or fail to build on previous successes.
With proper knowledge management, marketing teams can:
- Document campaign strategies, assets, and results in a structured format
- Record lessons learned during execution
- Create templates based on successful campaigns
- Make this institutional knowledge available to new team members
Consider a software company that documented each product launch campaign in their knowledge base. When a new product manager joined, they quickly reviewed previous launch campaigns, learning which messaging resonated with customers and which channels delivered the strongest results. This knowledge transfer happened without requiring meetings with the entire marketing team.
This approach transforms each campaign into a learning opportunity that improves future marketing efforts rather than an isolated event.
Marketing asset management
The volume of marketing assets created by marketing teams (logos, photos, videos, infographics, presentations) requires careful organization. When assets live in multiple locations, marketers waste time hunting for what they need.
A knowledge base with robust asset management capabilities allows teams to:
- Store all visual assets in a searchable repository
- Implement version control to prevent usage of outdated assets
- Organize assets by campaign, channel, or content type
- Set access permissions based on teams and roles
For example, a retail company’s marketing team structured their knowledge base to store all campaign visuals with standardized naming conventions and tags. Team members can quickly filter by product line, season, or channel to find exactly what they need without searching through multiple drives or requesting assets from colleagues.
This structured approach eliminates the “Do you have the latest version?” emails that consume marketing team bandwidth.
Content calendar and editorial planning
Content marketing requires careful planning and coordination across multiple stakeholders. When content plans live in spreadsheets with limited visibility, alignment breaks down.
Centralizing content planning documentation helps teams:
- Document editorial guidelines and standards in one accessible location.
- Create transparent content workflows visible to all stakeholders.
- Maintain publishing schedules across channels.
- Track content performance metrics and insights.
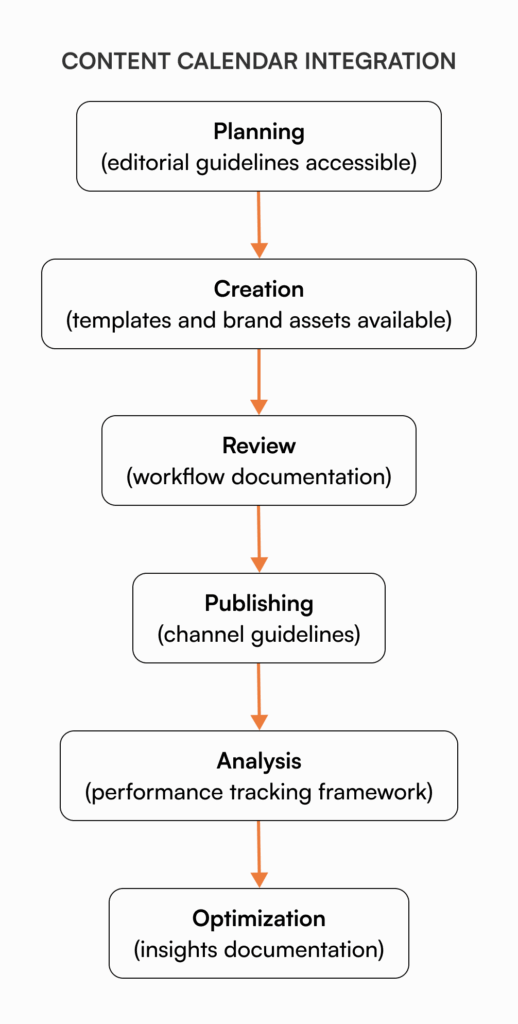
A healthcare organization uses their knowledge base to document the entire content lifecycle. Their editorial calendar links to specific guidance for each content type, approval workflows, and channel-specific requirements. This system ensures writers, designers, and approvers all follow consistent processes regardless of which team member is leading a particular content piece.
This visibility reduces misalignment and enables content teams to maintain consistent quality and cadence.
Competitor research database
Marketing teams gather valuable competitive intelligence that drives strategy. Without proper documentation, these insights remain isolated or get lost entirely.
A competitor research knowledge base allows teams to:
- Create structured profiles of key competitors
- Document competitive messaging and positioning
- Track competitor campaigns and channel strategies
- Share market analysis across departments
An e-commerce company maintains a dedicated section in their knowledge base with detailed competitor analyses. When planning quarterly campaigns, their marketing team reviews this centralized competitive intelligence to identify gaps in the market and opportunities for differentiation.
This approach creates a sustained competitive advantage rather than relying on fragmented observations. It transforms competitive intelligence from scattered observations into strategic assets that inform marketing decisions.
Marketing technology documentation
The modern marketing technology stack includes numerous platforms with complex configurations. When usage documentation exists only in the minds of power users, teams struggle to leverage these tools effectively.
Centralizing martech documentation helps teams:
- Create standard operating procedures for each platform
- Document configurations and integration points
- Build troubleshooting guides for common issues
- Record best practices for platform usage
This knowledge base reduces dependency on specific team members and ensures consistent tool utilization.
New hire onboarding
Marketing roles require specific knowledge about brand standards, processes, and tools. Without structured onboarding, new team members take longer to become productive contributors.
A knowledge base accelerates marketing onboarding by providing:
- Role-specific resource collections
- Self-service access to needed information
- Process documentation for critical workflows
- Brand and messaging guidelines in one location
This creates consistency in how new team members learn about marketing operations. Research from the Society for Human Resource Management indicates that it takes new hires 8-12 months to achieve full productivity in professional roles, making structured onboarding documentation essential for marketing teams.
Customer personas and segmentation details
Effective marketing relies on deep customer understanding, but persona documentation often lives in presentation decks rarely referenced after creation.
Centralizing customer insights helps teams:
- Maintain living customer persona documents
- Document segment characteristics and behaviors
- Store messaging frameworks aligned to each segment
- Make research findings accessible to inform future campaigns
This keeps customer understanding at the center of marketing activities rather than isolated in strategy documents.
Vendor and partner information
Marketing teams work with multiple agencies, freelancers, and technology vendors. When relationship details live in individual inboxes, collaboration becomes inefficient.
A knowledge base for external relationships helps document:
- Agency scopes and working processes
- Vendor contracts and capabilities
- Partner program details and requirements
- Contact information and relationship history
This documentation reduces disruption when team members change and ensures consistent vendor management.
Performance reporting templates
Marketing teams create regular performance reports for various stakeholders. Without standardized approaches, reporting consumes excessive time and lacks consistency.
Centralizing reporting knowledge helps teams:
- Define standard KPIs and calculation methodologies
- Create reusable reporting templates
- Document data sources and collection processes
- Build stakeholder-specific reporting frameworks
A B2B marketing team stores their reporting templates and analytics guidelines in their knowledge base. When preparing executive updates, team members follow standardized formats that ensure consistent metrics are presented each month. New team members can quickly learn how performance is measured without lengthy training sessions.
This approach transforms reporting from a time-consuming exercise into an efficient, value-adding process.
Consider Susan, a marketing manager who inherited quarterly reporting responsibilities when her predecessor left. Instead of recreating reports from scratch, she accessed the knowledge base’s reporting templates and immediately understood which metrics executives expected, how data should be presented, and where to source the information. What could have been weeks of confusion became a smooth transition.
How AllyMatter supports marketing knowledge management
Marketing teams need more than basic document storage – they need intelligent organization that matches how marketing work actually happens. AllyMatter addresses these specific marketing challenges through features designed for dynamic, collaborative teams.
- Flexible document organization with smart tags and categories that align with marketing workflows
- Granular access control for appropriate sharing with agencies and external collaborators
- Complete version tracking that maintains the history of evolving marketing assets and guidelines
- Intelligent search functionality that makes finding marketing assets and documentation straightforward
- Collaboration features that enable marketing teams to work together on documentation
The platform integrates seamlessly with existing marketing workflows, enhancing productivity without disrupting established processes.
What you can achieve with marketing knowledge management
An internal knowledge base transforms marketing operations by:
- Centralizing critical brand and campaign knowledge
- Preserving institutional marketing wisdom
- Streamlining collaboration with internal and external stakeholders
- Creating consistency in marketing execution
- Reducing time spent searching for information
Getting started with your marketing knowledge base
Implementing a marketing knowledge base starts with auditing your current knowledge assets and identifying high-value content to migrate first. Set up a structure that aligns with how your team searches for information, then migrate priority content. Train your team, establish knowledge champions, and create clear usage guidelines. Measure adoption and gather feedback to continuously optimize the system.
Marketing teams that implement these knowledge management practices can focus more on strategy and creative work rather than administrative challenges.
Ready to transform your marketing team’s knowledge management? Join our waitlist to be among the first to experience AllyMatter’s marketing-focused features.
Frequently asked questions
How can marketing teams ensure adoption of a new knowledge base?
Successful adoption starts with involving the team in setup, focusing on documenting the most-requested information first, and integrating the knowledge base into daily workflows. Leadership should model usage, recognize contributors, and make the knowledge base the default location for critical information.
What’s the difference between a digital asset manager and a marketing knowledge base?
While digital asset managers primarily organize visual files like images and videos, a marketing knowledge base encompasses all marketing knowledge including processes, guidelines, strategies, and assets. Many marketing teams need both, with the knowledge base often serving as the organizational framework that includes or connects to more specialized tools.
Which marketing processes benefit most from knowledge base documentation?
Processes with multiple stakeholders, frequent repetition, or high complexity gain the most from documentation. Campaign planning, content creation workflows, approval processes, and reporting procedures typically show the greatest improvement when thoroughly documented in a knowledge base.
How do you maintain knowledge base accuracy as marketing evolves?
Successful marketing knowledge bases implement regular review cycles, assign clear ownership of each document, and create update workflows triggered by marketing changes. The best systems include feedback mechanisms that allow team members to flag outdated information for review.
How do marketing teams balance accessibility with security in their knowledge base?
Marketing teams often work with external agencies and contractors while maintaining sensitive competitive information. A robust knowledge base should offer granular access controls that allow sharing brand guidelines with external partners while restricting access to strategic documents. Role-based permissions ensure team members see exactly what they need without compromising security.


