Last Tuesday, your finance team burned three hours digging through email threads looking for an expense policy that got updated months ago. Your newest support rep gave customers wrong troubleshooting steps because nobody knew where the current guides lived. This happens every day at growing companies. Critical information gets scattered across systems, buried in email chains, or stuck in people’s heads.
The solution isn’t just better organization; it’s a fundamental shift toward systematic knowledge management through a well-designed knowledge base. Let’s dig into what knowledge bases actually are, why they matter for growing companies, and how to implement them without creating more chaos.
What is a knowledge base?
A knowledge base is a centralized repository that captures, organizes, and makes accessible the collective knowledge of an organization. Think of it as your company’s external brain. A searchable system where critical information lives and stays put when people leave or the company grows.
Document storage just dumps files somewhere. Knowledge bases organize information through categories, tags, and metadata so people can actually find what they need. They support various content types – from standard operating procedures and policy documents to training materials and troubleshooting guides.
Research by Davenport and Prusak shows that knowledge bases work as structured systems that capture, store, and share knowledge within organizations, helping employees access and use information effectively.
Types of knowledge bases
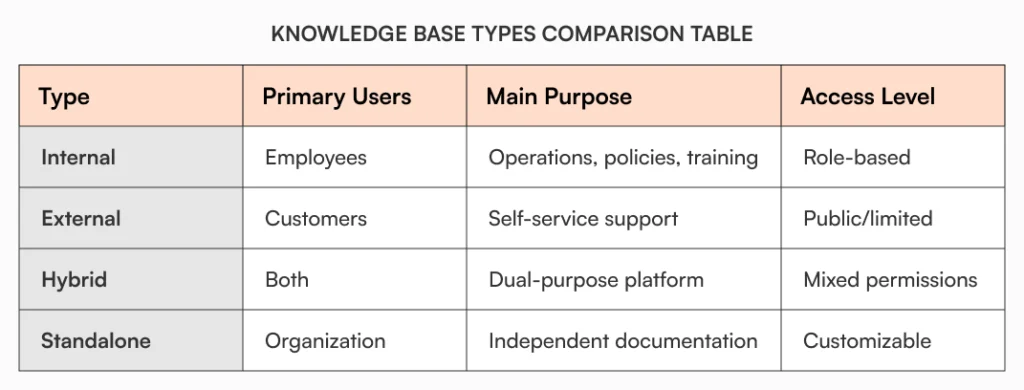
Internal knowledge bases serve your team. HR policies, SOPs, technical docs, training materials – everything your people need to do their jobs properly. These systems focus on operational efficiency, knowledge preservation, and enabling employee self-service within your organization.
They typically include role-based access controls to ensure sensitive information reaches only appropriate personnel while maintaining searchability across departments. Internal knowledge bases become particularly crucial as organizations scale, preventing knowledge silos and reducing dependency on individual team members for critical information.
Read our detailed guide on internal knowledge base.
External knowledge bases (often called help centers) enable customer self-service, allowing users to find answers without contacting support. Research shows that 91% of customers would use an online knowledge base if it were available and tailored to their needs.
These customer-facing systems focus on clear, accessible language and intuitive navigation to help users resolve issues independently. They typically feature FAQ sections, troubleshooting guides, and step-by-step tutorials designed to reduce support ticket volume while improving customer satisfaction.
Hybrid knowledge bases combine both internal and external functions, providing different access levels and content based on user permissions. These sophisticated systems allow organizations to maintain a single platform while serving multiple audiences – employees can access internal procedures and policies, while customers see only relevant self-service content.
Standalone knowledge bases operate independently of other business systems, providing dedicated documentation environments without requiring integration with existing tools. These self-contained systems offer complete control over the knowledge management environment and are particularly valuable for organizations with strict data isolation requirements.
Explore further: Standalone Knowledge Bases: The Complete Guide
Choosing the right platform approach
You’ve got plenty of choices when picking a knowledge base platform. Traditional solutions, cloud-based systems, open source options – the list goes on. Understanding these options helps ensure you choose the right foundation for your knowledge management strategy.

Traditional communication vs. knowledge bases
Many organizations struggle with choosing between traditional communication methods and dedicated knowledge management systems. Email has long been the default for information sharing, but it creates significant limitations as organizations grow. To understand why dedicated knowledge bases outperform email for organizational knowledge management, explore our complete analysis in email vs KB that examines the fundamental differences and strategic advantages of each approach.
Open source and flexible licensing options
For organizations seeking cost-effective solutions with maximum customization potential, open source platforms offer compelling advantages. These solutions provide transparency, community support, and the ability to modify systems according to specific organizational needs.
Organizations with specific licensing preferences can explore MIT or open source, licensed open source KBs for organizations that focus on permissive licensing models that offer maximum flexibility for customization and redistribution.
Related reading: Open Source Knowledge Bases for Organizations: A Global Guide
Global platform considerations
Knowledge base selection increasingly requires understanding global implementation patterns and regional considerations. Organizations expanding internationally or serving diverse markets need platforms that accommodate different languages, compliance requirements, and cultural preferences.
For detailed insights into global knowledge management trends and implementation strategies across different regions, explore our global guides to knowledge bases that cover fundamental concepts and worldwide best practices:
- Global Guide to Knowledge Bases – Part 1
- Global Guide to Knowledge Bases – Part 2
- Global Guide to Knowledge Bases – Part 3
- Global Guide to Knowledge Bases – Part 4
- Global Guide to Knowledge Bases – Part 5
Why every business needs a knowledge base
The cost of scattered information goes far beyond wasted time. According to McKinsey, employees spend nearly 20% of their workweek searching for internal information or tracking down colleagues for help. For a 100-person company, that’s equivalent to losing 20 full-time employees to information hunting.
Eliminating information silos
Information silos develop naturally as organizations grow. Different departments use different tools, critical knowledge remains trapped in individual minds, and processes vary across teams. A knowledge base creates a single source of truth, ensuring everyone works from the same information.
For example, Sarah from finance recently spent an entire afternoon recreating an expense report template because she couldn’t locate the standardized version. Unknown to her, the accounting team had developed the exact template she needed just two weeks prior, but it was buried in a department-specific folder. This scenario repeats across departments daily when information remains siloed.
Consider your operations team developing an innovative process improvement, but the documentation lives solely in someone’s personal notes. Meanwhile, another department struggles with the exact same challenge, unaware that a solution already exists. Knowledge bases prevent this costly duplication of effort.
Preserving institutional knowledge
According to Panopto research, 42% of institutional knowledge is unique to individual employees and isn’t documented elsewhere in the organization. When key personnel leave, they take years of accumulated wisdom with them unless it’s properly captured.
A well-maintained knowledge base ensures expertise stays with your organization regardless of personnel changes, supporting business continuity and reducing the impact of employee turnover. Understanding how lost knowledge translates directly to lost revenue helps organizations prioritize proper knowledge management as a strategic business investment rather than just an operational necessity.
Accelerating onboarding and training
Knowledge bases significantly accelerate the onboarding timeline by providing structured, accessible training materials and reference documentation. New employees can find answers independently instead of constantly interrupting colleagues, while managers spend less time on repetitive explanations.
Also, discover how AllyMatter helps your accelerate onboarding and increase new hire productivity.
Supporting compliance and risk management
According to a PwC survey, about 35% of risk executives view compliance and regulatory risk as the top barrier to their company’s growth. Knowledge bases help manage this risk by ensuring everyone follows current policies and maintaining audit trails for compliance purposes.
Explore more: Here’s Why Every Business Needs a Knowledge Base
Key benefits of implementing a knowledge base
Enhanced productivity and efficiency
When people can find what they need quickly, they spend time on work that matters instead of hunting for documents. Research shows that workers toggle between applications nearly 1,200 times daily, spending approximately four hours per week just reorienting themselves after switching contexts.
Knowledge bases fix this by putting everything in one searchable place. Teams find what they need in seconds rather than hours, keeping momentum on important projects.
Simplified automation and process management
Modern knowledge management extends beyond simple document storage to encompass automated workflows and intelligent process management. Organizations can significantly reduce manual overhead while improving consistency and accuracy through strategic automation.
Improved decision-making
Access to comprehensive, up-to-date information enables better decisions at every level. When teams can quickly reference historical data, previous decisions, and established procedures, they avoid repeating mistakes and build upon proven approaches.
Scalable knowledge sharing
As organizations grow, traditional knowledge sharing methods break down. Email becomes unmanageable, informal mentoring doesn’t scale, and critical information gets lost in chat tools. Knowledge bases provide a scalable foundation that grows with your organization.
Consistent customer experience
For customer-facing teams, knowledge bases ensure consistent, accurate responses regardless of which team member handles an interaction. This consistency builds trust and improves satisfaction while reducing the training burden on support staff.
Related reading: How Knowledge Bases Can Help Deflect Tickets
Essential features of effective knowledge bases
Intelligent search and organization
Even the most detailed knowledge base is worthless if people can’t find what they’re looking for. Effective systems provide powerful search capabilities that understand context and user intent, not just keyword matching. Smart categorization through tags, metadata, and custom categories ensures information remains discoverable as content volumes grow.
Also read: Scaling Your Knowledge Base: How AllyMatter Grows with Your Business
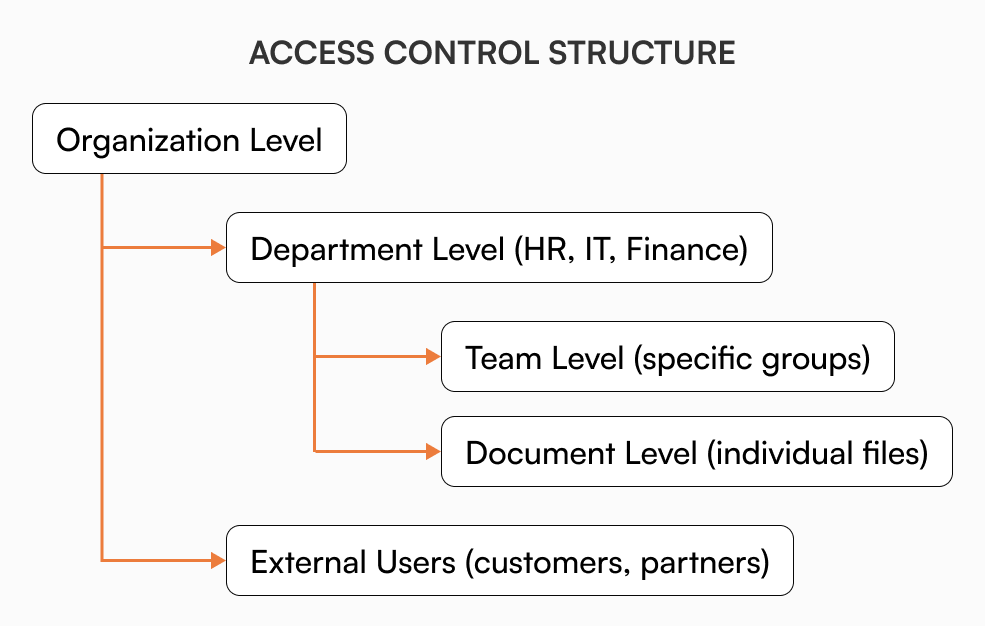
Access control and permissions
Growing organizations need granular control over who sees what information. Role-based permissions ensure teams access relevant content while protecting sensitive information. Effective access control adapts to organizational changes without creating bottlenecks, supporting collaboration while maintaining security.
Read more: Keep Your Docs Safe but Accessible.
Version control and audit trails
Documentation must evolve with your business, but tracking changes is crucial for accountability and compliance. Version control capabilities let you see how information has evolved, compare different versions, and restore previous content when needed.
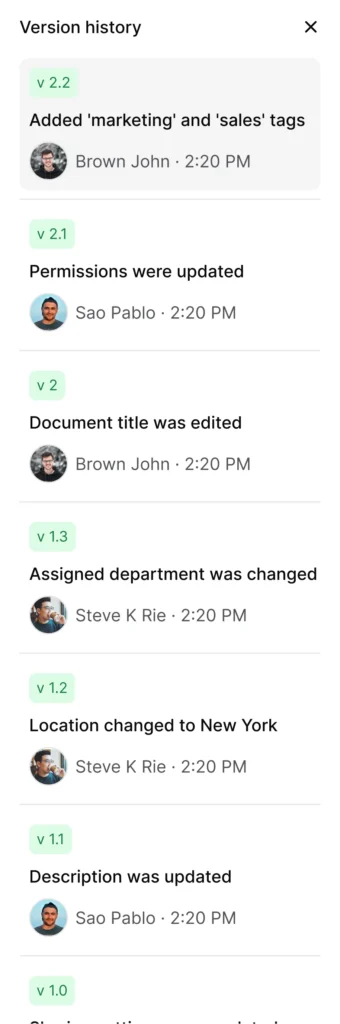
Comprehensive audit trails document who made changes, when they occurred, and why, supporting both operational continuity and regulatory requirements.
Read how AllyMatter’s comprehensive audit capabilities support both operational continuity and compliance requirements, by managing documentation history and traceability.
Collaboration tools
Knowledge creation should be collaborative, incorporating input from multiple stakeholders. Built-in commenting, discussion threads, and approval workflows streamline the content development process. These collaborative features transform knowledge base development from an isolated task into a team effort that captures collective expertise.
Integration capabilities
Knowledge bases shouldn’t exist in isolation. Integration with existing tools – project management platforms, communication systems, and business applications – ensures knowledge management fits naturally into existing workflows.
Implementation strategies for different organizational needs
HR departments
HR teams benefit enormously from centralized policy management, streamlined onboarding processes, and consistent employee communications. Knowledge bases can house everything from benefits information to compliance procedures, making HR resources easily accessible to all employees.
Employee self-service through knowledge bases reduces routine HR inquiries, freeing HR professionals to focus on strategic initiatives rather than answering repetitive questions about policies and procedures.
Related reading: Everything You Need to Know About Building a Knowledge Base for HR
IT teams
IT departments typically handle a broad spectrum of requests, from password resets to complex troubleshooting. Well-structured knowledge bases dramatically reduce ticket volumes by providing self-service options for common issues.
Technical docs, setup guides, and troubleshooting decision trees help users fix problems themselves. This frees up IT teams to work on complex challenges that actually need expert help.
Customer support
Support teams use knowledge bases both internally and externally. Internal documentation ensures consistent, accurate responses, while external knowledge bases enable customer self-service. According to Forrester, customers prefer knowledge bases over all other self-service channels, making external knowledge bases essential for modern customer experience strategies.
Related reading: How Knowledge Bases Can Help Improve Customer Service
Operations teams
Operations benefit from standardized procedures, quality control documentation, and process improvement tracking. Knowledge bases ensure everyone follows the same protocols while capturing improvements for organization-wide implementation.
Common implementation challenges and solutions
Overcoming adoption resistance
People resist new systems even when the old way clearly doesn’t work. They’ll spend 20 minutes searching through email instead of 30 seconds checking the knowledge base.
Address this by demonstrating clear value, starting with high-impact use cases, and making contribution easy rather than burdensome. Focus on solving real pain points rather than implementing technology for its own sake. When people see immediate benefits, adoption follows naturally.
Managing content quality
Knowledge bases can quickly become cluttered with outdated or inaccurate information. Establish clear ownership for different content areas, implement regular review cycles, and create processes for keeping information current.
Follow these content review rules:
- Gets used weekly? Keep it current.
- Monthly access? Consider combining with similar content.
- Nobody’s touched it in 90 days? Archive it or update it.
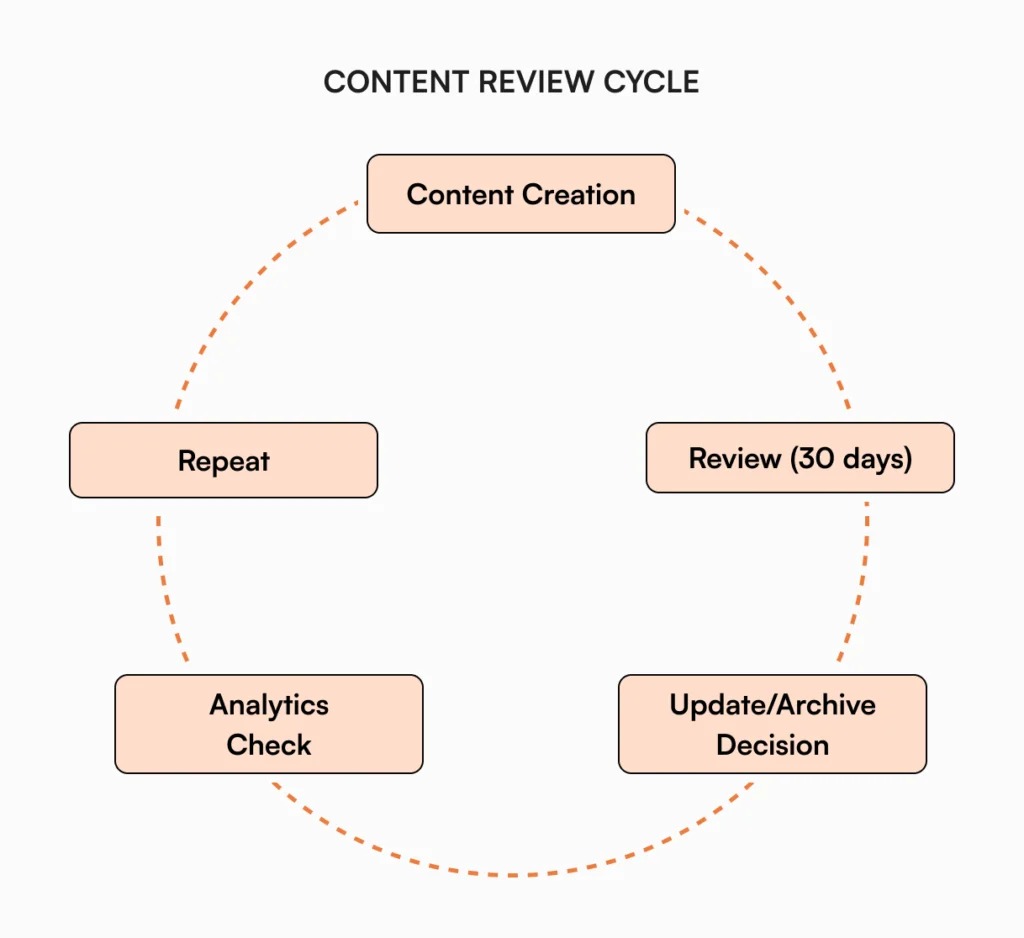
Quality control isn’t just about accuracy; it’s about maintaining trust in the system. Users who encounter outdated information quickly lose confidence in the entire knowledge base.
Also read: Knowledge Base Archiving: When and How to Archive Pages Strategically
Balancing structure with flexibility
Organizations need enough structure to keep information organized but sufficient flexibility to accommodate different content types and use cases. Avoid over-engineering initial implementations; start simple and evolve based on actual usage patterns.
Ensuring security and compliance
As knowledge bases grow, they often contain sensitive information requiring careful access management. Implement appropriate security measures from the beginning rather than trying to retrofit them later.
Measuring knowledge base success
Usage and engagement metrics
Track how people interact with your knowledge base through metrics like page views, search queries, and time spent on content. These indicators reveal which information is most valuable and where gaps might exist. Monitor search terms that yield no results; these represent unmet information needs and opportunities for content development.
Business impact indicators
Connect knowledge base usage to business outcomes like reduced support tickets, faster onboarding times, and improved customer satisfaction scores. These connections demonstrate ROI and justify continued investment.
Content performance analysis
Identify your most valuable content and understand why it performs well. Use these insights to improve other content and guide future development priorities.
The future of knowledge management
AI and automation integration
Artificial intelligence is transforming knowledge management through improved search capabilities, automated content suggestions, and intelligent categorization. Modern knowledge bases increasingly use AI to enhance user experience and reduce maintenance overhead.
However, AI enhancement requires high-quality, well-structured content as a foundation. Organizations that invest in proper knowledge base fundamentals will be best positioned to leverage these advancing technologies.
Also read: Make Your Knowledge Base Ready for LLMs & AI
Integration with business workflows
Knowledge bases are evolving from standalone repositories to integrated components of broader business systems. This integration ensures knowledge management becomes a natural part of existing workflows rather than an additional burden.
Automated workflow capabilities, from approval processes to content distribution, are becoming standard features that streamline knowledge management operations.
Explore: Understanding Document Workflows in AllyMatter: A Comprehensive Guide.
How AllyMatter supports growing organizations
While understanding knowledge base concepts is important, implementing them effectively requires the right platform designed specifically for growing organizations. AllyMatter addresses the unique challenges that scale-ups and growth-stage companies face when building comprehensive knowledge management systems.
- Centralized knowledge without complexity: AllyMatter eliminates information silos by bringing all your documentation into one intelligent, searchable platform. Unlike generic document storage solutions, our system provides smart organization through custom categories, metadata, and powerful search capabilities that actually improve as your content grows.
- Built-in governance and compliance: As your organization scales, compliance requirements become more complex. AllyMatter provides detailed audit trails, version control, and approval workflows that ensure accountability while simplifying regulatory compliance. Track every change, maintain proper documentation history, and demonstrate compliance efforts with built-in reporting capabilities.

- Flexible access control that grows with you: Growing organizations need sophisticated permission systems that adapt to changing structures. AllyMatter’s granular access controls ensure the right people see the right information while maintaining security. Role-based permissions, department-specific access, and document-level controls provide the flexibility needed for complex organizational structures.
- Collaborative knowledge creation: Transform knowledge development from isolated tasks into team efforts with built-in commenting, discussion threads, and collaborative editing features. AllyMatter makes it easy to capture collective expertise and ensure all relevant stakeholders contribute to critical documentation.
- Scalable foundation for the future: Unlike basic tools that break down as organizations grow, AllyMatter is designed to scale with your business. From startup documentation needs to enterprise-level knowledge management, our platform provides the features and flexibility needed to support long-term growth without requiring platform migrations.
AllyMatter helps growing companies build knowledge management systems that actually work, transforming scattered information into organized, accessible knowledge that drives operational efficiency and supports sustainable growth.
Building your knowledge management foundation
Successful knowledge base implementation requires more than just selecting the right technology. It demands a smart approach that considers organizational culture, content governance, and long-term scalability.
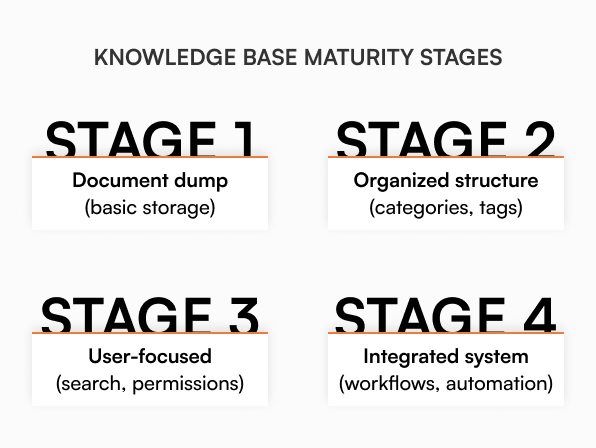
Start by identifying your most pressing information challenges and implementing solutions incrementally. Focus on high-impact areas where knowledge bases can provide immediate value, then expand based on success and learning.
Remember that knowledge management is an ongoing process, not a one-time project. The most successful organizations treat their knowledge bases as living systems that evolve with their business needs and growth trajectory.
Establish clear governance processes, assign content ownership, and create sustainable practices for keeping information current and valuable. These foundational elements determine long-term success more than any specific feature or technology choice.
Companies that win don’t hoard information. They make the right information accessible when people actually need it. A well-implemented knowledge base transforms scattered organizational knowledge into a strategic asset that supports growth, efficiency, and competitive advantage.
Whether you’re just starting to explore knowledge management or looking to improve existing systems, the principles and practices outlined in this guide provide a foundation for building knowledge bases that truly serve your organization’s needs and support sustainable success.
Ready to transform your organization’s knowledge management? Join our waitlist to be among the first to experience AllyMatter’s comprehensive knowledge base platform designed specifically for growing companies.
Frequently asked questions
How do I know if my organization needs a knowledge base?
If your people spend half an hour every day hunting for basic information, constantly ask coworkers for the same documents, or do things differently across departments, you need a knowledge base. Most companies realize this when email becomes completely unmanageable for sharing information.
What’s the best way to migrate existing documentation to a knowledge base?
Start with your most frequently accessed documents and critical processes. Audit existing content for accuracy, consolidate duplicate information, and prioritize based on business impact. Avoid migrating everything at once; focus on high-value content that solves immediate problems.
How can we maintain content quality as our knowledge base grows?
Establish content ownership for different areas, implement regular review cycles, and create clear guidelines for updates. Assign document stewards who are responsible for keeping information current, and use analytics to identify outdated or unused content for review.
What features should we prioritize when selecting a knowledge base platform?
Focus on robust search capabilities, flexible access controls, version tracking, and integration with existing tools. Ensure the platform can scale with your organization and provides analytics to measure usage and identify content gaps.


