Every support query that lands in your inbox represents more than just a question. It’s time taken away from strategic initiatives, a potential bottleneck in your workflow, and often, a question you’ve already answered before. For IT, HR, and support teams facing growing ticket volumes, this challenge hits particularly hard.
The frustration is familiar: team members solve the same printer connectivity issue for the fifth time this week, HR repeatedly explains the updated leave policy, or support teams walk yet another customer through password reset steps. These recurring questions aren’t just minor interruptions; they’re systematic drains on productivity and morale.
Knowledge bases offer a strategic solution to this problem, serving not just as information repositories but as powerful ticket deflection engines. By centralizing information in an accessible, searchable format, organizations can empower employees and customers to find answers independently, dramatically reducing repetitive support requests while improving satisfaction across the board.
High costs of recurring tickets
The impact of repetitive support tickets extends far beyond the immediate time spent answering them. According to BMC Software, the average service desk ticket cost across North America was $15.56 in 2016. When multiplied across dozens or hundreds of similar queries each month, the financial impact becomes substantial.
But the costs go deeper than just finances:
- Delayed resolution times as teams repeatedly research the same issues
- Knowledge inconsistency when different team members provide varying solutions
- Increased frustration for both support providers and those seeking help
- Critical work deprioritized as teams handle the constant influx of basic queries

Picture this scenario: A new expense reporting system is implemented across your organization. Without centralized documentation, IT and finance teams face dozens of daily tickets about submission procedures, while managers struggle to approve requests properly. The finance department falls behind on processing, creating a ripple effect throughout the company. Meanwhile, the dedicated knowledge holders become bottlenecks, pulled into endless troubleshooting sessions rather than advancing strategic projects.
A well-structured knowledge base directly addresses these pain points by providing a single source of truth for common questions, available whenever needed.
Key knowledge base elements that drive ticket deflection
Not all knowledge bases deliver the same results when it comes to ticket deflection. The most effective implementations share several critical elements that maximize self-service potential:
Intelligent search and organization
The foundation of effective ticket deflection is findability. Users must be able to quickly locate relevant information using natural language searches, category browsing, or tags. According to a study by Forrester Research, 53% of adults are likely to abandon their online purchase if they can’t find quick answers to their questions. This applies equally to internal knowledge bases. If employees can’t find information quickly, they’ll default to submitting a ticket.
Effective organization includes:
- Intuitive categorization by department, process, or topic
- Consistent tagging for cross-referencing related content
- Natural language search capability that understands variations in phrasing
Version control and real-time updates
Outdated information is sometimes worse than no information at all. When HR policies change or IT systems are updated, your knowledge base must reflect these changes immediately. With proper version tracking, teams can ensure they’re always accessing the most current information, eliminating tickets based on confusion over which procedure is current.
Cross-departmental accessibility
Knowledge rarely exists in isolation. The most effective knowledge bases break down information silos between departments, ensuring that interconnected processes are documented end-to-end. When an employee onboarding process involves both HR and IT steps, for example, having this information connected creates a seamless experience and prevents tickets that result from handoff confusion.
Rich media integration
Text alone often isn’t sufficient for complex processes. Knowledge bases that incorporate screenshots, videos, flowcharts, and interactive elements provide clearer guidance and better accommodate different learning styles.
For instance, an IT troubleshooting guide that includes a brief screen recording of the resolution process can be significantly more effective than text instructions alone, reducing follow-up questions and increasing successful self-resolution rates.
Consistent formatting and templates
Standardized formats for different types of knowledge articles create familiarity and improve navigation. When users know exactly where to find prerequisites, step-by-step instructions, and troubleshooting tips within any article, they can quickly extract the information they need without submitting clarification tickets.
Implementing self-service in different departments
Different teams face unique support challenges, but knowledge bases can be customized to address the specific needs of each department:
IT teams: Technical documentation that empowers
IT departments typically handle a broad spectrum of requests, from password resets to software troubleshooting. A well-structured knowledge base can dramatically reduce these tickets by providing:
- Step-by-step guides for common procedures like printer setup or VPN access
- Troubleshooting decision trees for identifying and resolving common errors
- Access management documentation explaining permission levels and request processes
- System update announcements with clear timelines and impact assessments
For example, a growing software company can implement detailed setup guides in their knowledge base for their development environment. This will result in fewer new developer onboarding tickets.
HR departments: Policy clarity and self-service
Human Resources teams often field repetitive questions about policies, benefits, and procedures. Knowledge bases streamline this by offering:
- Searchable policy documentation with clear version history
- Benefits explanations with interactive comparison tools
- Leave request procedures with required forms and approval workflows
- Onboarding checklists for both managers and new employees
Rather than emailing HR for clarification on the updated parental leave policy, employees can access the latest information themselves, complete with eligibility requirements and application procedures.
Customer support: Empowering users while reducing volume
For customer-facing teams, knowledge bases serve dual purposes; they help internal teams maintain consistency while offering customers direct access to information:
- Product documentation with feature explanations and use cases
- Troubleshooting guides for common issues organized by product area
- Account management procedures for billing and subscription changes
- FAQ collections addressing the most common customer inquiries
When support teams notice particular questions arising frequently, they can prioritize creating or improving knowledge articles on those topics, creating a virtuous cycle of continuous improvement and ticket reduction.
Measuring knowledge base impact on ticket deflection
Implementing a knowledge base is just the first step. Measuring its effectiveness is crucial for ongoing optimization and demonstrating ROI. These key metrics help quantify success:
Ticket volume trends
The most direct measurement is the change in ticket volume for specific categories after implementing related knowledge base content. Track both overall numbers and specific categories to identify where your knowledge base is most effective and where gaps might still exist.
Self-service ratio
This critical metric compares how many users view knowledge base articles versus how many submit support tickets. A growing ratio indicates increasing self-service adoption. Calculate this by dividing knowledge base views by the number of tickets submitted in the same period.
Search analytics
User search behavior provides invaluable insights:
- Most common search terms (indicating high-demand information)
- Failed searches (revealing content gaps)
- Search-to-content ratios (showing whether users find what they’re seeking)
Feedback mechanisms
Direct feedback from users helps assess quality beyond numbers:
- Article ratings (helpful/not helpful)
- Comments identifying unclear or incomplete information
- Suggestion mechanisms for new content needs
For example, a company can analyze their top 20 searched terms and create comprehensive guides for each, thereby reducing related tickets significantly. This will free their IT team to focus on infrastructure improvements instead of repetitive support.
Overcoming common knowledge base implementation challenges
Even with clear benefits, knowledge base implementations face several common obstacles. Addressing these proactively improves adoption and effectiveness:
Content maintenance and currency
The greatest threat to knowledge base effectiveness is outdated information. Establish clear ownership and regular review cycles for all content, with automated reminders when content approaches review dates. Implement a transparent version history system so users can see when information was last updated and by whom.
Balancing depth versus accessibility
Technical experts often create highly detailed documentation that overwhelms casual users. Structure content in layers, providing quick answers up front with expandable sections for those needing deeper information. Use clear, consistent language and avoid jargon where possible.
Encouraging team adoption and contribution
Knowledge bases thrive with broad contribution, but teams accustomed to answering one-off questions may resist documentation efforts. Create incentives for knowledge sharing, integrate documentation into existing workflows, and celebrate improved metrics to build momentum.
Consider implementing a simple process where closing a ticket includes asking, “Should this be added to our knowledge base?” This single question can drive continuous improvement in documentation coverage.
Integrating with existing workflow tools
Knowledge bases shouldn’t exist in isolation. Look for integration opportunities with:
- Ticketing systems (to suggest relevant articles before submission)
- Communication platforms (for easy sharing of knowledge articles)
- Collaboration tools (to streamline contribution workflows)
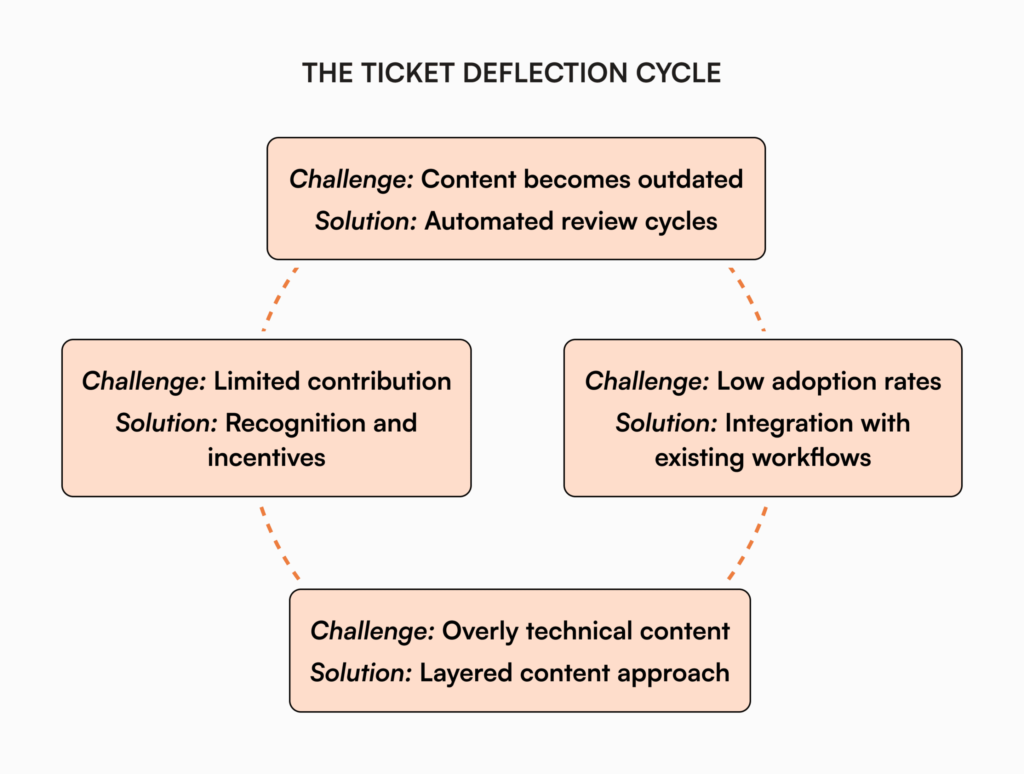
The easier it is to access and contribute to the knowledge base within existing workflows, the more effective it becomes at deflecting tickets.
Building a knowledge-centered culture
The most successful knowledge base implementations extend beyond technology to create organizational cultural shifts. When knowledge sharing becomes a valued practice rather than an additional task, the impact multiplies:
- Support teams proactively contribute solutions as they discover them
- Subject matter experts recognize documentation as amplifying their expertise, not draining their time
- Managers acknowledge and reward knowledge contributions in performance reviews
- New employees are trained to check the knowledge base first before submitting tickets
This cultural transformation turns knowledge from a static resource into a dynamic organizational asset that continuously improves through collective input and refinement.
By implementing a strategic knowledge base focused on ticket deflection, organizations don’t just reduce support volumes. They fundamentally transform how teams work together, preserve institutional knowledge, and deliver consistent experiences to both employees and customers.
How AllyMatter helps
AllyMatter’s knowledge management platform is specifically engineered for maximum ticket deflection impact. The platform’s intelligent search with smart tags and custom categories ensures teams find answers in seconds, not minutes. Granular access control means each department sees only relevant information, eliminating confusion and improving adoption.
The platform’s seamless workflow integration allows knowledge articles to surface automatically during ticket creation, while comprehensive analytics track which content drives the highest deflection rates. With enterprise-grade security and automated version control, AllyMatter transforms scattered tribal knowledge into a unified self-service ecosystem that consistently reduces support volume while preserving institutional expertise.
Ready to see how AllyMatter can reduce your team’s ticket volume? Join the waitlist.
Frequently asked questions
How long does it typically take to see results from a new knowledge base implementation?
You can typically see initial results within the first 30-60 days after implementing a knowledge base. Quick wins often come from documenting answers to your most common support questions first. However, more significant ticket deflection (20%+ reduction) usually takes 3-6 months as content matures, teams adapt their workflows, and users become accustomed to self-service. Organizations that integrate their knowledge base with existing tools and actively promote its use tend to see faster adoption and results.
What types of content should be prioritized first in a knowledge base?
Start by analyzing your ticket data to identify your highest-volume request categories. These represent your biggest opportunity for immediate impact. Common priorities include:
- Password reset and access procedures
- New employee onboarding steps
- Common software troubleshooting guides
- Frequently asked policy questions
- Standard request processes (like equipment requests or benefit changes)
Focus on creating comprehensive solutions for these top issues before expanding to less common scenarios.
How can we encourage employees to use the knowledge base instead of submitting tickets?
Success requires both technical integration and cultural change. Integrate knowledge suggestions directly into your ticket submission workflow, train department heads to reference articles in team communications, and track adoption metrics by department. Consider implementing a brief “knowledge-first” policy where common issues require checking the knowledge base before ticket submission. Organizations that celebrate self-service wins and share time-savings metrics typically see faster adoption across teams.
What’s the difference between a knowledge base and a company wiki?
While both store organizational information, they serve different purposes. Wikis typically focus on collaborative editing and broad information sharing but often lack structured organization and specialized features for support contexts. Knowledge bases are purpose-built for support scenarios with:
- More robust search capabilities optimized for problem-solution matching
- Structured templates for consistent documentation
- Version control for compliance and accuracy
- Integration with support workflows and ticketing systems
- Analytics specifically designed to measure support deflection
- Access controls for sensitive information
Many organizations use both: wikis for general collaboration and knowledge bases for structured support content.
How often should knowledge base content be reviewed and updated?
The optimal review cycle depends on how frequently the underlying information changes:
- Mission-critical or frequently changing content (like security procedures or active projects): Monthly review
- Standard operational procedures: Quarterly review
- Relatively stable policies or reference information: Semi-annual review
Regardless of schedule, implement a system where major changes (like software updates or policy revisions) automatically trigger content reviews. Some knowledge management platforms offer automated review reminders based on content age or usage patterns.