In today’s fast-paced corporate world, having a reliable and efficient human resources (HR) ticketing system is paramount. However, the success of any system is often tied to the quality of its documentation. Good documentation aids in the smooth implementation, use, and maintenance of the system. Besides, it drives adoption and maximizes your technology investment.
If you’re tasked with creating documentation for an HR ticketing system, here’s a step-by-step guide to help you craft a comprehensive, user-friendly guide.
Define your system’s purpose and goals
Before you start writing, have a clear understanding of what the HR ticketing system is designed to achieve. Is it for handling employee grievances, processing payroll queries, or managing leave applications? Or perhaps it’s a combination of multiple functionalities? Knowing the system’s purpose will shape the content and tone of your documentation.
Once you’re clear on your system’s purpose, you’re ready to introduce it effectively to your users.
Start with an introduction
Begin your documentation with an introductory section that:
- Explains the purpose and scope of the HR ticketing system.
- Provides a brief overview of the main components and features.
- Lists the intended audience, whether it’s HR professionals, general employees, or both.
Outline the user interface
Provide a detailed walkthrough of the system’s user interface:
- Use screenshots to illustrate different sections and features.
- Highlight the primary navigation menus, buttons, and fields.
- Ensure clarity by using annotations or arrows to point out crucial elements.
For example: The dashboard displays your open tickets in the left panel, with priority levels color-coded (red for urgent, yellow for medium priority, green for low priority).
Create step-by-step guides for common processes
Break down typical tasks into step-by-step instructions. For an HR ticketing system, these might include:
- How to create a new ticket.
- How to categorize and prioritize tickets.
- Steps for escalating a ticket.
- The process for closing and archiving completed tickets.
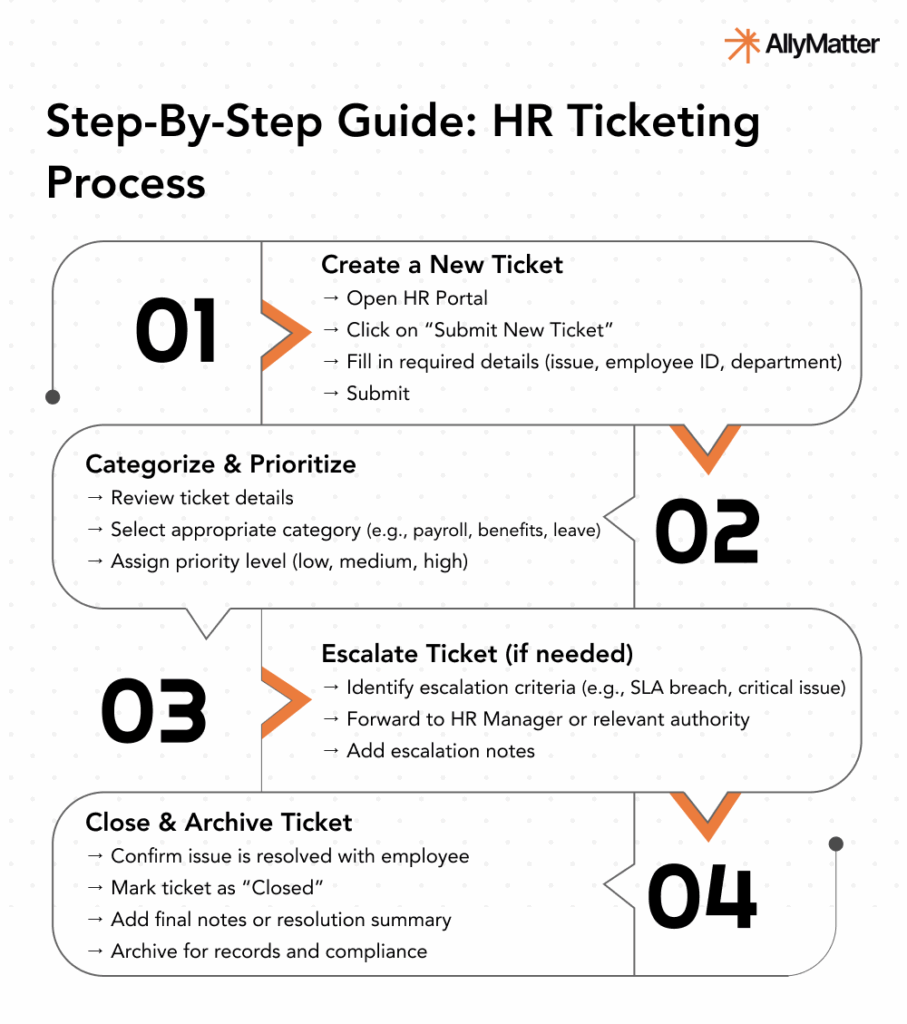
Use clear, concise language, and consider including screenshots for each step to visually guide the user.
Connect your systems: Integration considerations
Modern HR departments rely on multiple systems working together. Your documentation should address:
- How the ticketing system integrates with other HR platforms (HRIS, payroll, LMS, etc.)
- Data flow between systems (what information transfers automatically vs. manually)
- Authentication methods (Single Sign-On options)
- Troubleshooting integration issues
Be specific about the integration capabilities. For example: When an employee updates their address in the HRIS, this information automatically syncs with the ticketing system within 24 hours.
Empower users with troubleshooting section
Even the most well-designed systems can face issues. Dedicate a section to common problems users might encounter and provide solutions for each:
- List frequent error messages and their meanings.
- Describe common user mistakes and how to avoid or correct them.
- Provide steps for system resets or basic debugging if applicable.
Ensure compliance throughout documentation
Given the regulatory requirements surrounding HR functions, include:
- How the system helps maintain compliance with relevant laws (GDPR, HIPAA, etc.)
- Documentation retention requirements and capabilities
- Audit trail functionality
- Required approval workflows for sensitive processes
Highlight security and data privacy measures
In an age where data privacy is critical, your documentation should assure users of the system’s security measures:
- Explain how personal and sensitive data is protected.
- Outline the data backup and recovery processes.
- Provide guidelines on setting strong passwords and maintaining user confidentiality.
Enable decision with metrics and reporting
Help HR teams leverage data-driven insights:
- Document available reports and dashboards
- Explain how to create custom reports
- Provide examples of how metrics can inform decision-making
For example: By tracking “Time to Resolution’ for benefits questions, you can identify which benefits policies may need clearer employee communication.
Address accessibility
Your HR ticketing system should be inclusive and accessible to all users, including those with disabilities:
- Provide tips on using the system with screen readers or other assistive technologies.
- Describe any built-in accessibility features.
- Offer alternatives for users who might face challenges in accessing the system.
Tailor documentation for different user roles
Different stakeholders need different information:
- HR administrators need complete system knowledge.
- Managers need to know how to approve requests and view team metrics.
- Employees need focused guides on submitting and tracking their tickets.
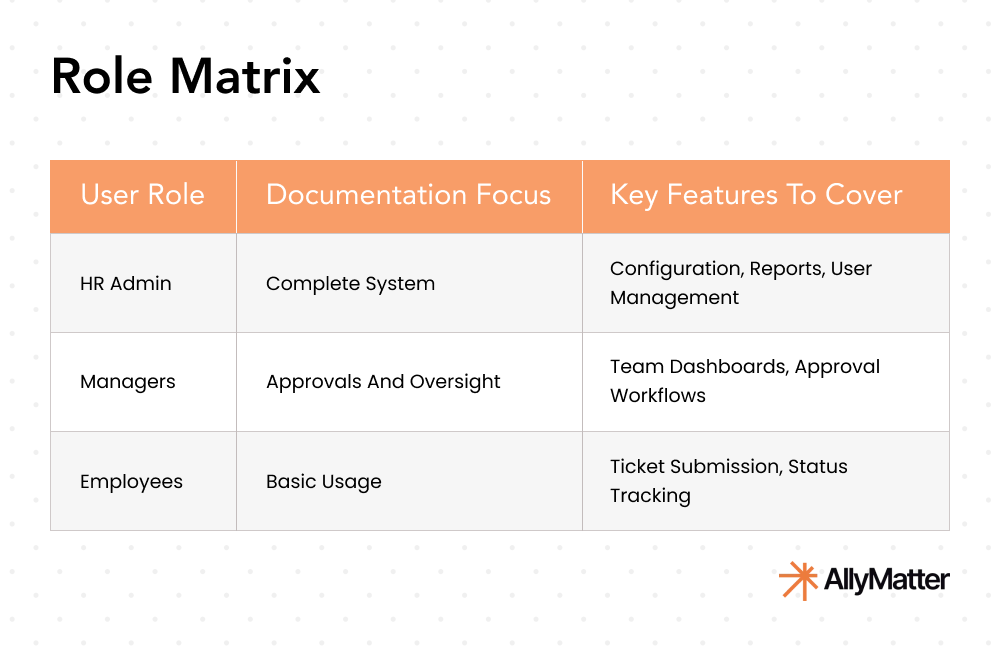
Create role-specific quick-start guides that contain only what each user type needs to know.
Optimize for mobile
With remote and hybrid work becoming standard, document mobile functionality:
- Differences between desktop and mobile interfaces
- Mobile-specific features and limitations
- Tips for efficient mobile use
Emphasizing mobile is particularly relevant, as HubEngage indicates 85% of employees favor smartphones for workplace HR communications.
FAQs and best practices
A well-crafted FAQ section can quickly address common user queries. Gather feedback from initial users or beta testers to compile this section. Additionally, suggest best practices to ensure efficient use of the system, such as:
- Proper ticket categorization techniques.
- Guidelines for clear communication within tickets.
- Tips for tracking and following up on pending tickets.
Build a clear glossary of terms
To ensure comprehension, include a glossary that defines any technical or industry-specific terms used throughout your documentation.
Provide contact information
Despite the best documentation, users will sometimes need direct assistance. Ensure they know how to get help:
- List contact details for technical support, including email, phone numbers, and hours of operation.
- Include response time expectations.
- Offer links to online resources or forums if available.
Update the documentation regularly
As the HR ticketing system evolves, so should your documentation. Regularly review and update the guide to reflect system changes, additional features, or feedback from users. Document version history clearly so users know when information was last updated.
Read more: Building a Future-Proof Internal Knowledge Base
Seek feedback and test the documentation
Before finalizing, ask a diverse group of users to test the documentation. Their feedback can identify missing information or areas of confusion.
How AllyMatter supports comprehensive HR documentation
Creating and maintaining HR ticketing system documentation becomes significantly easier with a centralized knowledge management platform. AllyMatter’s intelligent organization features help you structure documentation with smart tags and custom categories, making it simple for users to find exactly what they need.
The platform’s version control ensures your documentation stays current without losing important historical information. When your HR system updates, you can track changes, compare versions, and maintain an audit trail of all documentation modifications.
Role-based access control means you can provide the right level of detail to each user type while protecting sensitive information. HR administrators see comprehensive setup guides, while employees access streamlined how-to content tailored to their needs.
With built-in collaboration features, your HR team can work together on documentation updates, ensuring accuracy and completeness across all materials.
Building documentation that drives HR success
Creating comprehensive documentation for an HR ticketing system requires a mix of technical knowledge, empathy for the end-user, and an eye for detail. Remember, the primary goal is to simplify the user’s experience, making it as straightforward and hassle-free as possible. With a well-crafted guide, you not only empower users but also reduce the strain on support teams, leading to an overall efficient and effective HR ticketing system.
Ready to streamline your HR documentation process? Join AllyMatter’s waitlist to discover how centralized knowledge management can transform your HR operations.
FAQs about HR ticketing system documentation
How often should HR ticketing system documentation be updated?
Review your documentation quarterly and update immediately after any system changes. Set calendar reminders to check for outdated screenshots, process changes, or new features that need documentation.
What’s the difference between user guides and process documentation?
User guides focus on how to navigate and use the system interface, while process documentation explains the workflow, decision points, and business rules behind each action. Both are essential for comprehensive documentation.
How do you ensure documentation stays relevant as your system evolves?
Assign documentation ownership to specific team members, create update workflows triggered by system changes, and gather regular feedback from users about gaps or outdated information.
What documentation format works best for different user roles?
Administrators need comprehensive technical guides, managers require approval workflow summaries, and employees benefit from visual quick-start guides. Tailor format and depth to each audience’s needs.
How can you measure the effectiveness of your HR system documentation?
Track metrics like support ticket volume for documented processes, time to resolution for common issues, and user feedback scores. A decrease in basic how-to questions indicates effective documentation.


